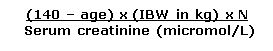Renal Dosing
General Principles
General Principles
-
Many medicines are excreted by the kidneys and require dose adjustment in renal impairment to avoid toxicity.
-
Antimicrobial dosage depends on the type and severity of the infection, sensitivity of the causative organism and the general condition of the patient. For severe infections the higher end of the dose range should be used.
-
For some drugs, although the size of the maintenance dose is reduced, it is important to still give a loading dose when recommended.
-
Caution if concomitant hepatic and renal impairment – a further reduction in dosing may be indicated.
-
There is inconsistency among published sources of information on drug dosing in renal impairment. Recommendations in these guidelines are largely derived from The Renal Drug Database (RDD), which in some cases may be higher than the manufacturer’s recommendations in the Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC) and the BNF.
-
Doses of Antimicrobials in Renal impairment are outlined in Table . Antimicrobials marked with an asterix have significant differences in dosing between reference sources. In some cases a dose range is given – the higher end of the range should be used for severe infections. See HPRA.ie for licensed dose recommendations.
-
“Usual” dose refers to the dose and interval recommended for adults with normal renal and hepatic function in GUH Antimicrobial Guidelines and GUH Intravenous Administration Guide.
Assessing Renal Function
Assessing Renal Function
1. Published information on the effects of renal impairment on drug elimination is usually stated in terms of creatinine clearance, calculated using Cockcroft & Gault equation, as a surrogate for GFR.
2. The Evolve system reports renal function as eGFR (estimated glomerular filtration rate) normalised to a body surface area of 1.73m 2 , calculated using the CKD-EPI equation.
3. Although the two measures of renal function are NOT interchangeable, for most drugs and for most adult patients of average build and height, eGFR (rather than CrCl) can be used to determine dosage adjustments.
4. The BNF now uses eGFR for dose reduction for most (but not all) drugs, as does the Dosing Table for Antimicrobials in Renal impairment . Exceptions to the use of eGFR, where calculation of creatinine clearance (Cockcroft & Gault equation) is recommended, include:
- Elderly patients aged 75 years and over
- Patients at extremes of muscle mass (BMI less than 18 kg/m 2 or greater than 40 kg/m 2 )
-
Nephrotoxic drugs and drugs with a narrow therapeutic index that are mainly renally excreted. The BNF doesn’t specify which drugs but examples specified in the Dosing Table include:
- Aminoglycosides (e.g. Amikacin, Gentamicin, Tobramycin)
- Vancomycin
- Foscarnet
- Ganciclovir
- Valganciclovir
5. Using serum creatinine to derive eGFR has a number of limitations; serum creatinine levels are dependent on muscle mass and diet, therefore estimates should be interpreted with caution in certain individuals (such as the elderly, body builders, amputees, in muscle-wasting disorders and vegans)—estimates will be higher or lower than the true value.
6. Creatinine-derived measurements are also not useful in periods of rapidly changing renal function (e.g. critical care) or in patients with Acute Kidney Injury (AKI).
7. In principle, in the acutely critically ill patient with AKI, antimicrobials with wide therapeutic indices and minimal safety concerns e.g. beta lactams should/may be given at full dose for the first 24-48h. Regular monitoring of renal function is advised in acutely ill patients to ensure drug use and dosing is appropriate.
8. Dosing should be assessed on an individual patient basis, balancing risk versus benefit, and taking urine output and clinical picture into account.
9. The gentamicin calculator incorporates a creatinine clearance (CrCL) calculator, which calculates CrCl (ml/min) using Cockcroft and Gault . This may be used for dose adjustment for other antimicrobials.
Cockcroft and Gault Equation
|
Cockcroft and Gault Equation Creatinine Clearance (CrCl) (ml/min) 1.Calculate Ideal Body Weight (IBW) in kg (see below) 2. If actual body weight < IBW, use actual body weight in this equation
N = 1.23 males & 1.04 females |
|
Ideal Body Weight (IBW) (kg) = Male: 50kg + (2.3kg x inches over 5 feet) OR 50kg + (0.9kg x cm over 152cm) Female: 45.5kg + (2.3kg x inches over 5 feet) OR 45.5kg + (0.9kg x cm over 152cm) |
Renal Replacement Therapy
Renal Replacement Therapy
- Intermittent Haemodialysis (IHD) : Assume GFR <10ml/min . Many drugs are removed by haemodialysis. If dialysed, it is recommended to time administration to take place post dialysis and at the same time every day including dialysis days (to avoid the need to give a supplemental dose post dialysis). In GUH medium flux filters are most commonly used for intermittent haemodialysis, although high flux filters may be used for some patients.
- A haemodialysis unit guideline summarises dosing of Vancomycin, CefAZOLin, Daptomycin & Gentamicin for patients with chronic renal impairment on IHD.
- Continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT): Recommendations for dosing of antimicrobials for patients on CRRT in critical care are not covered in these guidelines. In GUH, continuous venovenous haemodiafiltration (CVVHDF) is the type of continuous renal replacement used. ICU pharmacist is available for advice during working hours.
Dosing Table for Antimicrobials in Renal Impairment
Dosing Table for Antimicrobials in Renal Impairment
- This dosage adjustment table is intended for use in the treatment of infection of hospitalised patients only.
- It recommends dose adjustment using the patient’s eGFR value (or Creatinine Clearance using Cockcroft and Gault (CrCL) if specified).
- Please refer to General principles and Assessing Renal function . Clinical judgement should be used alongside any estimates derived from equations or suggested dose adjustments.
- For some medicines, the renal dose information is presented as a dose range –use the higher end of the dose range for severe infections. Antimicrobials marked with an *asterix have significant differences in dosing between reference sources.
- In situations where a range of dosing is recommended, patient, indication and severity of infection need to be considered. Specific factors include age, immune function, degree of renal impairment, risk of adverse effects etc.
- More detailed information on some antimicrobials is available in GUH IV guides . See links in individual monographs.
- “Usual” dose refers to the dose and interval recommended for adults with normal renal and hepatic function in GUH Antimicrobial Guidelines and GUH Intravenous Administration Guide.
|
Doses of Antimicrobials in Renal Impairment (Adults) |
|||||||
|
Antimicrobial
|
eGFR (ml/min/1.73m 2 ) |
Comment |
|||||
|
Aciclovir IV If obese, use ideal or adjusted body weight to calculate dose - See IV guideline (link) for details. |
eGFR 25 to 50 Usual dose every 12h |
eGFR 10 to 25 Usual dose every 24h |
eGFR <10 50% of usual dose every 24h |
Maintain adequate hydration. Risk of crystalluria / neurological reactions increased. |
|||
|
Amikacin Reserve antimicrobial
|
CrCl < 80 : Reduce dose. See Amikacin Dosing Table |
Monitor levels. Must use CrCl (not eGFR). |
|||||
|
* Amoxicillin IV/PO |
eGFR 10 to 50 No dose adjustment required
|
eGFR <10 250mg to 1g q8h High dose regimens e.g. endocarditis & listeria meningitis: max 2g q8h |
|
||||
|
Amphotericin Liposomal AmBisome ® Reserve antimicrobial |
No dose adjustment required |
Highly nephrotoxic – monitor renal function, potassium and magnesium |
|||||
|
Anidulafungin Reserve antimicrobial |
No dose adjustment required |
|
|||||
|
Artesunate |
No dose adjustment required |
|
|||||
|
Atovaquone |
eGFR 10 to 50 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR <10 Usual dose with caution |
Monitor more closely in renal impairment. |
||||
|
Azithromycin |
Usual but use with caution if eGFR <10 |
33% increase in systemic exposure to azithromycin in patients when GFR<10 |
|||||
|
Aztreonam Reserve antimicrobial |
eGFR 30 to 50 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR 10 to 30 Usual first dose, then 50% of usual dose |
eGFR <10 Usual first dose, then 25% of usual dose |
Nebulised: Dose as in normal renal function |
|||
|
Benzylpenicillin |
eGFR 20 to 50 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR 10 to 20 600mg to 2.4g q6h |
eGFR <10 600mg to 1.2g q6h |
Increased risk of neurotoxicity (seizures) in renal impairment |
|||
|
Use higher doses for severe infection only e.g. endocarditis |
|||||||
|
Caspofungin Reserve antimicrobial |
No dose adjustment required |
|
|||||
|
* CefALEXin |
eGFR 40 to 50 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR 10 to 40 500mg q8h |
eGFR <10 500mg q12-24h |
|
|||
|
* CefAZOLin
|
eGFR 35-54 Usual dose q8h
|
eGFR 11-34 1 – 2g q12h
|
eGFR <10 1 – 2g q24h
Haemodialysis |
High doses in severe infection as per ID/Micro only Caution - Increased risk of convulsions in renal impairment |
|||
|
CefoTAXime Reserve antimicrobial |
eGFR 5 to 50 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR <5 50% of usual dose For severe/life-threatening infection contact Micro/ID |
Reduce dose further if concurrent hepatic and renal failure. |
||||
|
CefTAROLine Reserve ‘red-light‘ antimicrobial
Standard dose: 600mg q12h
High dose: 600mg q8h |
eGFR 31 to 50
400mg q12h
400mg q8h
|
eGFR 15 to 30
300mg q12h
300mg q8h
|
eGFR <15
200mg q12h
200mg q8h
|
|
|||
|
CefTAZidime Reserve antimicrobial |
eGFR 31 to 50 1g to 2g q12h |
eGFR 16 to 30 1g to 2g q24h |
eGFR 6 to 15 500mg to 1g q24h eGFR <5 500mg to 1g q48h |
|
|||
|
CefTAZidime/ Avibactam (Zavicefta) Reserve ‘red-light‘ antimicrobial
On Micro or ID approval only |
eGFR 31 to 50 1.25g q8h |
eGFR 16 to 30 0.94g q12h
|
eGFR 6 to 15 0.94g q24h End stage renal disease including on haemodialysis 0.94g q48h |
|
|||
|
CefTOLOzane/ Tazobactam (Zerbaxa) Reserve ‘red-light‘ antimicrobial
On Micro or ID approval only |
eGFR <50 Reduce dose. Renal dose depends on indication. See IV Guide. |
|
|||||
|
CefTRIAXone Reserve antimicrobial |
eGFR 10 to 50 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR <10 Usual max 2g q24h
Meningitis only: 2g BD (see comment)
|
High dose (in meningitis in eGFR <10 to be discussed with Micro/ID. Max 2 g q24h if severe renal impairment in combination with hepatic impairment |
||||
|
CefUROXime IV |
eGFR 20 to 50 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR 10 to 20 750mg to 1.5g q12h |
eGFR <10 750mg to 1.5g q24h |
|
|||
|
* CefUROXime PO |
No dose adjustment required |
|
|||||
|
Chloramphenicol Reserve antimicrobial |
eGFR 10 to 50 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR <10 No dose adjustment required - but use only if no alternative. Discuss with Micro/ID |
Monitor levels in renal impairment (but not routinely available). See IV guide for additional information |
||||
|
* Ciprofloxacin IV/PO Reserve antimicrobial |
eGFR 30 to 50 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR 10 to 30 50 to 100% of usual dose
|
eGFR <10 50% of usual dose but if severe infection discuss with Micro or ID (may consider higher dose for short period) |
Higher end of dose range for severe infection should be discussed with Micro/ ID. Caution-Higher risk of tendon injury in renal impairment - see Quinolone warning in the prescribing principles section |
|||
|
* Clarithromycin IV/PO
|
eGFR 30 to 50 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR<30 250 to 500mg q12h. Use higher end of dose range for severe infection. |
Avoid if severe hepatic failure also present. May cause vomiting if eGFR <10 |
||||
|
Clindamycin IV/PO |
No dose adjustment required- but see comment if eGFR <10 |
Dosage reduction or monitoring may be necessary in severe renal impairment |
|||||
|
Co-amoxiclav IV |
eGFR 30 to 50 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR<30 1.2g q12h |
|
||||
|
* Co-amoxiclav PO |
No dose adjustment required |
|
|||||
|
Colistin IV Reserve ‘red-light‘ antimicrobial
Conventional dosing (Cystic Fibrosis) (1-2 Million International Units q8h) |
CrCl <20 Reduce dose. Renal dose depends on indication. See IV Guide.
|
Must use CrCl (not eGFR). |
|||||
|
Colistin IV Reserve ‘red-light‘ antimicrobial
High dose regimen (non-Cystic Fibrosis) (9 Million International Units, then 4.5 Million International Units q12h) On Micro or ID approval only |
CrCl <50 Reduce dose. Renal dose depends on indication. See IV Guide. |
Must use CrCl (not eGFR). |
|||||
|
* Co-trimoxazole IV/PO doses are expressed based the combination of trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
Treatment doses only
|
eGFR 30 to 50
No dose adjustment required |
eGFR 15 to 30
PJP : Usual dose for 3 days, then 30mg/kg q12h
Other indications: 50% of dose |
eGFR <15 (Use only if haemodialysis facilities available) PJP : 30mg/kg q12h
Other indications: Avoid if possible if levels cannot be monitored (or use 50% of dose if ID/Micro approved) |
Monitor levels in renal impairment (but not routinely available) |
|||
|
Dapsone |
eGFR 20 to 50 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR 10-20
No dose adjustment required. Use with caution |
eGFR <10 50-100mg daily. Use with caution. No dose reduction is required for malaria prophylaxis. |
Regular blood counts in renal impairment |
|||
|
Daptomycin Reserve ‘red-light‘ antimicrobial
On Micro or ID approval only |
eGFR 30 to 50 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR <30 Usual dose q48h |
Caution in renal impairment- monitor renal function & CPK closely if eGFR <80 |
||||
|
Doxycycline
|
No dose adjustment required |
|
|||||
|
Erythromycin IV/PO
|
No dose adjustment required |
Increased risk of ototoxicity in renal impairment especially at high doses. Max 1.5g daily in severe renal impairment |
|||||
|
Ethambutol
|
eGFR >30 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR <30 15 - 25mg/kg (Max 2.5g) 3 times/week |
Preferably avoid in renal impairment. Monitor levels if eGFR <30 (but not routinely available) |
||||
|
Fidaxomicin Reserve ‘red-light‘ antimicrobial
On Micro or ID approval only |
No dose adjustment required |
Use with caution in severe impairment |
|||||
|
Flucloxacillin IV/PO
|
eGFR 10 to 50 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR <10 Usually max 1g q6h but may require 2g q6h if recommended by Micro or ID e.g. for endocarditis |
Use with caution if concomitant liver impairment/ consider lower doses. Accumulation of electrolytes can occur |
||||
|
Fluconazole IV/PO
|
eGFR 10 to 50 1st dose: No dose adjustment required Subsequent doses: 50-100% of usual dose |
eGFR <10 50% of usual dose |
|
||||
|
Foscarnet |
Reduce dose. See IV Guide. |
Must use CrCl (not eGFR). Maintain adequate hydration. |
|||||
|
Fosfomycin PO Reserve antimicrobial On Micro or ID approval only |
eGFR 10 to 50 Uncomplicated UTI: 3g as a single dose |
eGFR <10 Avoid |
|
||||
|
Fosfomycin IV Reserve ‘red-light‘ antimicrobial
On Micro or ID approval only |
eGFR<40 Reduce dose according to indication. See IV Guide. |
SPC advises use with caution in renal impairment |
|||||
|
Fusidic Acid |
No dose adjustment required |
|
|||||
|
Ganciclovir |
CrCl <70 Reduce dose. See IV Guide. |
Must use CrCl (not eGFR). Maintain adequate hydration. |
|||||
|
|
CrCl < 80 : Reduce dose as per GAPP app calculator CrCl <10 on haemodialysis : See Haemodialysis Dosing Guidelines |
Monitor levels. Must use CrCl (not eGFR). |
|||||
|
Isavuconazole Reserve ‘red-light‘ antimicrobial On Micro or ID approval only |
No dose adjustment required |
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring may be required. Discuss with ID/Micro |
|||||
|
Isoniazid |
eGFR 10 to 50 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR <10 200 to 300mg q24h |
|
||||
|
Itraconazole PO |
No dose adjustment required |
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring may be required. Discuss with ID/Micro |
|||||
|
Itraconazole IV |
eGFR 30 to 80 Use with caution |
eGFR<30 Avoid |
IV vehicle may accumulate in renal impairment. |
||||
|
Levofloxacin IV/PO Reserve ‘red-light‘ antimicrobial
On Micro or ID approval only |
eGFR 20 to 50 500mg stat, then 250mg q12h |
eGFR 10 to 20 500mg stat, then 125mg q12h |
eGFR <10 500mg stat, then 125mg q24h |
Caution-Higher risk of tendon injury in renal impairment - see Quinolone warning in the prescribing principles section |
|||
|
Linezolid IV/PO On Micro or ID approval only |
No dose adjustment required Monitor FBC closely if eGFR <10 |
Caution in CrCl <30. Monitor platelets and for serotonin syndrome in renal impairment |
|||||
|
Meropenem Reserve ‘red-light‘ antimicrobial On Micro or ID approval only |
eGFR 26 to 50 500mg to 2g q12h |
eGFR 10 to 25 500mg to 1g q12h |
eGFR <10 500mg to 1g q24h |
Higher end of dose range for CNS / MDRO infection should be discussed with Micro/ ID. |
|||
|
Meropenem-Vaborbactam Reserve ‘red-light‘ antimicrobial
On Micro or ID approval only |
eGFR 20 to 39 1g/1g q8h |
eGFR 10 to 19 1g/1g q12h |
eGFR <10 500mg/500mg q12h |
|
|||
|
Metronidazole IV/PO |
No dose adjustment required |
|
|||||
|
Moxifloxacin IV/PO On Micro or ID approval only |
No dose adjustment required |
Caution-Higher risk of tendon injury in renal impairment - see Quinolone warning in the prescribing principles section |
|||||
|
Nitrofurantoin |
eGFR <45 Contraindicated. However, a short 3 to 7 day course may be used with caution in certain patients with an eGFR of 30 to 44 - to treat lower UTI with suspected/proven multidrug resistant pathogens when the benefits of nitrofurantoin are considered to outweigh the risks of side effects. |
May be ineffective in eGFR <60ml/min (RDD) due to inadequate urinary concentration; risk of peripheral neuropathy and blood dyscrasias. Monitor for pulmonary adverse events |
|||||
|
* Ofloxacin
|
eGFR 10 to 50 200 to 400mg q24h
|
eGFR <10 100 to 200mg q24h
|
Caution-Higher risk of tendon injury in renal impairment - see Quinolone warning in the prescribing principles section |
||||
|
Oseltamivir Treatment dose |
CrCl 31 to 60 30mg q12h |
CrCl 11 to 30 30mg q24h |
CrCl ≤10 30mg one dose |
(Dose in CrCl <10) Use CrCl if available; otherwise use eGFR |
|||
|
Oseltamivir Prophylaxis dose |
CrCl 31 to 60 30mg q24h |
CrCl 11 to 30 30mg q48h |
CrCl ≤10 30mg one dose, repeat after 7 days |
(Dose in CrCl <10) Use CrCl if available; otherwise use eGFR |
|||
|
Oxytetracycline |
e GFR 10 to 50 No dose adjustment required (but see comment) |
eGFR <10 250mg q6h |
Avoid if possible in renal impairment May exacerbate renal failure. Use only if essential |
||||
|
Pentamidine |
eGFR 10 to 50 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR <10 PJP Severe infection : 4mg/kg once daily IV for 7-10 days, then 4mg/kg on alternate days to complete the course of at least 14 doses PJP Non-severe infection : 4mg/kg IV on alternate days to complete the course of at least 14 doses |
|
||||
|
Phenoxymethyl-penicillin |
No dose adjustment required |
|
|||||
|
Piperacillin/ tazobactam |
eGFR 20 to 40 4.5g q8h |
eGFR <20 4.5g q12h |
|
||||
|
Posaconazole IV/PO Reserve antimicrobial |
Oral: Usual IV: eGFR<50: Avoid IV if possible (use oral), unless benefit of IV outweighs risk. |
IV vehicle may accumulate in renal impairment Therapeutic Drug Monitoring may be required. Discuss with ID/Micro |
|||||
|
Pyrazinamide |
eGFR 30 to 50 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR <30 25 - 30 mg/kg 3 times/week |
|
||||
|
Quinine
|
Oral: No dose adjustment required IV for treatment of malaria: see IV guide |
|
|||||
|
Rifampicin |
eGFR 30 to 50 No dose adjustment required |
eGFR <30 50 to 100% of usual dose TB : Give usual dose |
Use with caution in renal impairment if dose above 600mg daily, elderly or co-existing liver impairment |
||||
|
Teicoplanin Reserve antimicrobial |
eGFR 30 to 80 Give usual dose on days 1 to 4, then give usual dose q48h |
eGFR <30 Give usual dose on days 1 to 4, then give usual dose q72h |
Levels are not routinely available |
||||
|
Tigecycline Reserve ‘red-light‘ antimicrobial
|
No dose adjustment required |
|
|||||
|
Tobramycin
|
CrCl < 80 : Reduce dose. See GAPP app calculator |
Monitor levels. Must use CrCl (not eGFR). |
|||||
|
* Trimethoprim |
eGFR 15-30 Use normal dose for treatment – See Comment. |
eGFR <15 50-100% of normal dose |
May cause temporary rise in creatinine due to competition for renal secretion rather than a fall in CrCl, therefore avoid in those where acute rises in creatinine would complicate the clinical picture. Can cause hyperkalaemia, do not use in patients with CrCl<30ml/min where hyperkalaemia is a problem or if they are on other medications which can cause hyperkalaemia (e.g. ACE inhibitor, spironolactone) |
||||
|
ValACIclovir |
Reduce dose according to indication and renal function HSV: eGFR <30: Reduce dose Herpes zoster: eGFR <50: Reduce dose CMV prophylaxis: eGFR <75: Reduce dose See Renal Drug Database http://medinfogalway/renal-drug-database-log-detailshttp://www.renaldrugdatabase.com/ |
Maintain adequate hydration |
|||||
|
ValGANCIclovir |
CrCl <60 Reduce dose. See Renal Drug Database and/or specialist centre advice. www.renaldrugdatabase.com |
Must use CrCl (not eGFR). Maintain adequate hydration |
|||||
|
Vancomycin IV Reserve antimicrobial |
CrCl <50 : Reduce dose as per GAPP app calculator CrCl <10 on haemodialysis : See Haemodialysis Dosing Guidelines
|
Monitor levels. Must use CrCl (not eGFR) |
|||||
|
Voriconazole IV/PO Reserve antimicrobial |
Oral: No dose adjustment required IV: eGFR<50: Avoid IV if possible (use oral), unless benefit of IV outweighs risk. |
IV vehicle may accumulate in renal impairment Therapeutic Drug Monitoring may be required. Discuss with ID/Micro |
|||||
|
Antimicrobials marked with an *asterix have significant differences in dosing between reference sources |
|||||||
Vancomycin, CefAZOLin, Daptomycin & Gentamicin Dosing in Haemodialysis
|
Vancomycin, CefAZOLin, Daptomycin & Gentamicin Dosing Guidelines for Patients on Intermittent Haemodialysis |
|||||
|
Vancomycin
|
Weight
|
Loading dose |
Maintenance dose 750mg with each dialysis During latter part of dialysis, by infusion
|
Administration For inpatients, administer in haemodialysis unit and record on inpatient drug chart See IV guide for more information on administration
|
Monitoring Not usually necessary to hold the dose pending levels unless previous level high or toxicity suspected |
|
|||||
|
<50kg |
750mg |
||||
|
50-69kg |
1g |
||||
|
70-100kg |
1.5g |
||||
|
>100kg |
2g |
||||
|
CefAZOLin |
No loading dose required |
Give 2g/2g/3g three times weekly with each dialysis: 2g when next dialysis 2 days later, and 3g when next dialysis 3 days later |
Post dialysis |
None required |
|
|
Daptomycin |
No loading dose required |
Give 6/6/9 mg/kg three times weekly with each dialysis: 6mg/kg when next dialysis 2 days later, and 9mg/kg when next dialysis 3 days later |
Post dialysis |
None required |
|
|
Gentamicin |
2mg/kg to max 160mg
Use ABW, unless ABW >20% above IBW, then use dosing wt = IBW + 0.4 (ABW-IBW)* |
1mg/kg with each dialysis (max 80mg)
Use ABW unless ABW >20% above IBW, then use dosing wt = IBW + 0.4 (ABW-IBW)* |
Post dialysis |
|
|
|
*IBW – ideal body weight; ABW – actual body weight. IBW (kg) = 50 (45.5 for women) + (2.3 x inches over 5 feet) Further Information: Vancomycin: 80-90% excreted unchanged by the kidneys. Not significantly removed by conventional HD, removal increased by high flux HD. Gentamicin: 100% excreted unchanged by the kidneys. 30% removed during 4 hour HD Developed by GUH Pharmacy & Nephrology Depts Ref: IDSA Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of intravascular catheter-related infection. Clin Infect Dis 2009;49:1-45 |
|||||
References
References
- The Renal Drug Database www.renaldrugdatabase.com Accessed Feb 2021
- BNF accessed online via Medicines Complete Feb 2021
- Health Products Regulatory Authority. Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC): www.HPRA.ie
- The Sanford Guide to Antimicrobial Therapy Digital Update Accessed Feb 2021
- Johns Hopkins POC-IT ABX Guide. The Johns Hopkins University Accessed Feb 2021
- GUH IV Administration Guide
- Renal dosing of antibiotics: Are we jumping the gun? Clinical Infectious Diseases, 68 (9). 1596-1602 May 2019
- Nottingham University Hospital Antimicrobial Doses for Adults in Renal Impairment September 2019 https://www.nuh.nhs.uk/download.cfm?doc=docm93jijm4n629.pdf&ver=19071
Acknowledgements
Written by Marie Tierney & Dr. Úna NíRiain May 2012, Updated March 2021.
Reviewed by pharmacists and nephrologists in GUH, PUH. Approved by Antimicrobial Stewardship Team.