Renal Dosing (Adults)
Download / Print Section as PDFN.B. Estimates of GFR will not be accurate when the patient has an Acute Kidney Injury i.e. if the creatinine is rising or falling. The full clinical picture should always be taken into account.
Acute Kidney Injury
- For detailed information on antimicrobial dosing in Acute Kidney Injury, please see 'Critical Illness' reference on Medicines Complete, www.medicinescomplete.com . This is available free of charge on all HSE desktops and is also available on your smartphone via www.hselibrary.ie , please contact the HSE Library directly for an account if you do not already have one.
- A loading or initial dose of antimicrobial therapy should be administered as soon as possible in sepsis or septic shock (ideally within the first hour of presentation).
- Even in renal dysfunction, the full dose of beta-lactams should be used for at least the first dose and potentially the first 24 to 48 hours unless patient is frail, elderly, or has very low body-weight (Critical Illness). Contact Pharmacy for advice if needed.
- Any dose reduction of beta-lactams in response to AKI needs to be undertaken with caution ; much AKI seen in critical care is related to sepsis. The apparent Vd of beta-lactams can increase in sepsis and septic shock. The therapeutic consequences of underdosing antimicrobials in these patients may be severe and there is generally considered to be a wide margin of error before toxicity. Underdosing may lead to treatment failure and resistance. Due to these factors, it is common practice within critical care areas to administer standard doses for the first 24 to 48 hours.
- For potential nephrotoxins , e.g. gentamicin , vancomycin , check LH Guidelines as well as Critical Illness Reference. Also use clinical judgement with regard to dose. Contact Pharmacy for advice if needed.
- In patients presenting with an AKI, it is the acute changes in kidney function that must be considered and used to guide dose adjustments, rather than categories of function.
- During AKI, serum creatinine levels lag behind the development of the injury and progress of recovery. As creatinine rises, estimates of GFR will overestimate renal function and as creatinine falls and kidney function improves, estimates of GFR will underestimate renal function (BNF).
References:
- Critical Illness, www.medicinescomplete.com, accessed 4/3/24
- British National Formulary, www.medicinescomplete.com, accessed 4/3/24.
Chronic Kidney Disease
Calculate Creatinine Clearance
These tables apply to adult patients with chronic kidney disease only. They do not apply to patients on dialysis or those with acute kidney injury.
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Aciclovir IV |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 25 – 50 ml/min : 5 – 10mg/kg every 12 hours |
|
GFR 10 – 25 ml/min : 5 – 10mg/kg every 24 hours |
|
GFR < 10 ml/min : 2.5 – 5mg/kg every 24 hours |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Aciclovir ORAL |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 25 – 50 ml/min : Simplex: Usual dose; Zoster: Usual dose |
|
GFR 10 – 25 ml/min : Simplex: 200mg 4 times a day; Zoster: 800mg every 8 hours |
|
GFR < 10 ml/min : Simplex: 200mg every 12 hours; Zoster: 800mg every 12 hours |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 30 – 50 ml/min : 10mg/kg daily |
|
GFR 10 – 30 ml/min : 5mg/kg daily |
|
GFR < 10 ml/min : 3mg/kg STAT |
|
NB. Check trough level 16 – 24 hours after first dose. Trough < 5mg/L. If renal function stable, check trough level every 3 doses. If renal function abnormal or unstable, check trough level daily and wait for result unless patient acutely septic – in this case, contact Dr for advice. REVIEW DURATION OF AMIKACIN AS SOON AS POSSIBLE. |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Amoxicillin IV / ORAL |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 10 – 50ml/min : Usual dose |
|
GFR < 10 ml/min : 250mg – 1g every 8 hours (max 6g per day in endocarditis) |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Anidulafungin |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
No dose adjustment required in renal impairment |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Aztreonam |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 30 – 50 ml/min : Usual dose |
|
GFR 10 – 30 ml/min : 1 – 2g loading dose, then 50% of usual dose [note – maximum daily dose 8g if normal renal function] LH: Usual practice 1g TDS IV |
|
GFR < 10 ml/min : 1 – 2g loading dose, then 25% of usual dose [note – maximum daily dose 8g if normal renal function] LH: Usual practice 500mg TDS IV |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Benzylpenicillin |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 20 – 50 ml/min : Usual dose |
|
GFR 10 – 20 ml/min : 600mg to 2.4g every 6 hours |
|
GFR < 10 ml/min : 600mg to 1.2g every 6 hours |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Cef-AL-exin |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 30 – 50 ml/min : Usual dose |
|
GFR 10 – 30 ml/min : 250mg – 500mg every 8 to 12 hours |
|
GFR < 10 ml/min : 250mg – 500mg every 12 to 24 hours |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Cef-AZ-olin |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR > 35 ml/min: Normal dose every 8 hours |
|
GFR 11 – 34 ml/min: 50% of dose every 12 hours |
|
GFR < 10 ml/min: 1 to 2g daily. |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Cef-O-taxime |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 5 – 50ml/min : Usual dose |
|
GFR < 5 ml/min : 50% of dose at usual frequency |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Cef-TAZ-idime |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 31 – 50 ml/min :1g – 2g every 12 hours |
|
GFR 16 – 30 ml/min :1g – 2g every 24 hours |
|
GFR 6 – 15 ml/min : 500mg – 1g every 24 hours |
|
GFR < 5 ml/min : 500mg – 1g every 48 hours |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Cef-TRI-axone |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 10 – 50ml/min : Usual dose |
|
GFR < 10 ml/min : Maximum dose 2g every 24 hours |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Cef-UR-oxime IV |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 20 – 50ml/min : Usual dose |
|
GFR 10 – 20ml/min: 750mg – 1.5g every 12 hours |
|
GFR < 10ml/min: 750mg – 1.5g every 24 hours |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Ciprofloxacin IV / ORAL |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 30 – 50 ml/min : Usual dose |
|
GFR 10 – 30 ml/min : 50 – 100% of usual dose |
|
GFR < 10 ml/min : 50% of usual dose |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Clarithromycin IV / ORAL |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 30 – 50 ml/min : Usual dose |
|
GFR < 30ml/min : 250mg – 500mg every 12 hours |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Clindamycin IV / ORAL |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
No dose adjustment required in renal impairment |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Co-amoxiclav IV |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 30 – 50 ml/min : Usual dose |
|
GFR < 30 ml/min : 1.2g every 12 hours |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Co-amoxiclav ORAL |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
No dose adjustment required in renal impairment |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Co-trimoxazole IV / ORAL Treatment doses only Note Trimethoprim causes a functional increase in creatinine |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 30 – 50 ml/min : Usual dose |
|
GFR 15 – 30 ml/min : 50% of dose; PCP: 60mg/kg every 12 hours for 3 days then 30mg/kg every 12 hours |
|
GFR < 15 ml/min : 50% of dose; PCP: 30mg/kg every 12 hours **Only to be given if haemodialysis facilities available** |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Daptomycin |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 30 – 50 mL/min: Usual dose |
|
GFR < 30 mL/min : Usual dose 48 hourly |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Doxycycline |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
No dose adjustment required in renal impairment |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Erythromycin IV / ORAL |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
No dose adjustment required in renal impairment |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Flucloxacillin IV / ORAL |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 10 – 50ml/min : Usual dose |
|
GFR < 10 ml/min : Maximum 4g per day |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Fluconazole IV / ORAL |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
No dose adjustment required for single dose therapy |
|
GFR 10 – 50 ml/min : 50 – 100% of usual dose |
|
GFR < 10 ml/min : 50% of usual dose |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Gentamicin IV ONCE DAILY |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 10 – 50 ml/min : 3mg/kg once daily |
|
GFR < 10 ml/min : 1.5mg/kg stat, redose when level < 1mg/L |
|
NB. Check trough level 16 – 24 hours after first dose. Trough < 1mg/L. If renal function stable, check trough level every 3 doses. If renal function abnormal or unstable, check trough level daily and wait for result unless patient acutely septic – in this case, contact Dr for advice. REVIEW DURATION OF GENTAMICIN AS SOON AS POSSIBLE. |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Levofloxacin IV / ORAL |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 20 – 50 ml/min : 500mg stat, then 250mg every 12 hours |
|
GFR 10 – 20 ml/min : 500mg stat, then 125mg every 12 hours |
|
GFR < 10 ml/min : 500mg stat, then 125mg every 24 hours |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Linezolid IV / ORAL |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
No dose adjustment required in renal impairment. Use with caution when CrCl < 10 mL/min and monitor FBC closely. Metabolites with MAOI activity may accumulate in renal failure, monitor patients closely . |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Meropenem |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 26 – 50 ml/min : 500mg – 2g every 12 hours. For severe or CNS infections, can use 1g every 8 hours. |
|
GFR 10 – 25ml/min : 500mg – 1g every 12 hours or 500mg every 8 hours |
|
GFR < 10 ml/min : 500mg – 1g every 24 hours |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Metronidazole IV / ORAL |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
No dose adjustment required in renal impairment |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Nitrofurantoin |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 45 – 60 ml/min : Usual dose, use with caution |
|
GFR 30 - 45 ml/min : Contra-indicated. An expert group from the MHRA has advised nitrofurantoin may be used with caution as short-course therapy for lower UTI in patients with eGFR 30–44 mL/min/1.73m 2 to treat resistant pathogens , when the benefits may outweigh the risks. |
|
GFR < 30 ml/min : Avoid |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Oseltamivir |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 30 – 60 ml/min: Usual dose |
|
GFR 10 - 30 ml/min: Treatment: 75 mg once daily or 30 mg twice daily. Prophylaxis: 75 mg every 48 hours or 30 mg once daily. |
|
GFR < 10 ml/min: Treatment: 75 mg as a single dose. Prophylaxis: 30 mg once a week (2 doses). |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Phenoxymethylpenicillin |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
No dose adjustment required in renal impairment |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Piperacillin with Tazobactam |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 40 to 50 ml/min: Usual dose |
|
GFR 20 to 40 ml/min : 4.5g every 8 hours |
|
GFR < 20 ml/min : 4.5g every 12 hours |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Rifampicin |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 10 – 50ml/min : Usual dose |
|
GFR < 10 ml/min : 50 – 100% of usual dose |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Sodium Fusidate |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
No dose adjustment required in renal impairment |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Vancomycin IV |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
GFR 20 – 50 ml/min : 25mg/kg STAT dose, then 15mg/kg every 24 hours starting approx. 24 hours after STAT dose (No loading dose if pregnant) |
|
GFR < 20 ml/min : 25mg/kg STAT dose. Check trough level daily and wait for result. Re-dose with 15mg/kg when trough < 20mg/L and adjust further doses based on trough level results. (No loading dose if pregnant) |
|
N.B. Check trough level within one hour before dose on day 3 (pre-4 th or 5 th dose for twice or three times daily dosing). Trough level 15 – 20 mg/L. |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Voriconazole IV |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
When GFR < 50 ml/min, accumulation of the intravenous vehicle, sulphobutylether beta cyclodextrin sodium occurs. Use oral voriconazole unless a risk benefit assessment justifies use of IV. Voriconazole has 96% oral bioavailability. |
|
References |
|
|
Antimicrobial |
|
Voriconazole ORAL |
|
Adult Renal Dose Adjustment |
|
No dose adjustment required in renal impairment |
|
References |
|
Assessing Renal Function
-
Published information on the effects of renal impairment on drug elimination is usually stated in terms of creatinine clearance (CrCl), calculated using the Cockcroft and Gault Equation.
-
In some cases, renal function may be reported on the basis of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) using the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formula.
-
The two equations are NOT interchangeable, however there is relatively good correlation between them for adult patients of average build and height, and either could be used for the majority of drugs.
- Creatinine clearance using the Cockcroft and Gault Equation should be calculated for drugs with a narrow therapeutic index , such as gentamicin and vancomycin, and for dose reduction of all drugs in patients at extremes of body weight (BMI < 18kg/m 2 or > 40kg/m 2 ).
- N.B. Estimates of GFR will not be accurate when the patient has an acute kidney injury (AKI), i.e. if the creatinine is rising or falling. The full clinical picture should always be taken into account.
- During AKI, serum creatinine levels lag behind the development of the injury and progress of recovery. As creatinine rises, estimates of GFR will overestimate renal function and as creatinine falls and kidney function improves, estimates of GFR will underestimate renal function.
Cockcroft and Gault Equation:
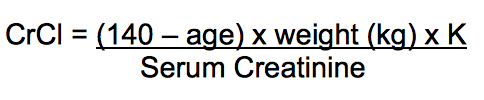
K = 1.23 for males and 1.04 for females
Which weight to use for CrCl calculation?
If Body Mass Index (BMI) < 30kg/m 2 , use actual weight to calculate CrCl
If BMI > 30kg/m 2 , use Obese Dosing Weight (ODW) to calculate CrCl
BMI = Weight(kg)/Height(m) 2
Ideal Body Weight (IBW) (kg) = R + 2.3kg for every inch over 5ft
R = 50 for males and 45.5 for females
ODW (kg) = IBW + 0.4(Actual weight – IBW)
References
-
Health Products Regulatory Authority. Summary of Product Characteristics for each product available from www.hpra.ie , accessed 01/05/18.
-
Ashley C and Dunleavy A [Editors]. The Renal Drug Database. UK: Radcliffe Publishing Limited; 2014. Available from www.renaldrugdatabase.com , accessed 9/1/2023.
-
John Hopkins ABX Guide, www.hopkinsguides.com , accessed 25/01/23.
-
BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. British National Formulary. Available from www.medicinescomplete.com , accessed 30/04/18.
-
Beaumont Hospital Antimicrobial Guidelines, 2023. On file in OLOL Pharmacy.
-
McKenna C. Medicines Information Enquiry on which weight to use for creatinine clearance, 2014. On file in OLOL Pharmacy.

